 esophagus
esophagus
M o r e
 H e y , c o o l !
H e y , c o o l !
e s o p h a g u s
i n f o !
e s o p h a g u s
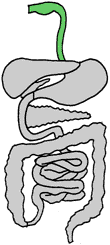
![]() The pharynx is where air and food passages cross. In adult human beings,
the esophagus is about 25 centimeters long. Swallowing includes a complex set of
reflexes that close off the opening into the nasal passages and windpipe, which is
also known as the trachea, This forces the food to move into the esophagus.
When these reflexes, for some reason,
fail to occur in the proper order, choking occurs. Food is moved down through the
esophagus into the stomach by rhytmic sequences of waves of the smooth muscle that
is located in the lower two thirds of the esophagus. These rhytmic sequences of
waves of muscular contraction in the walls of a tube are called peristalisis.
Humans are able to swallow upside down because the movement of food through the esophagus
is primarily caused by these peristaltic contractions.
The pharynx is where air and food passages cross. In adult human beings,
the esophagus is about 25 centimeters long. Swallowing includes a complex set of
reflexes that close off the opening into the nasal passages and windpipe, which is
also known as the trachea, This forces the food to move into the esophagus.
When these reflexes, for some reason,
fail to occur in the proper order, choking occurs. Food is moved down through the
esophagus into the stomach by rhytmic sequences of waves of the smooth muscle that
is located in the lower two thirds of the esophagus. These rhytmic sequences of
waves of muscular contraction in the walls of a tube are called peristalisis.
Humans are able to swallow upside down because the movement of food through the esophagus
is primarily caused by these peristaltic contractions.
![]() The lower esophageal (cardiac) sphincter controls the exit of food from the esophagus
to the stomach. It prevents the food in the stomach from moving back up the esophagus
by contracting. Heartburn occurs when the sphincter is not closed properly, because
the food backs up into the esophagus, and the acid coating it causes a burning
sensation. Heartburn often occurs during pregnancy because the digestive organs are
displaced far upward.
The lower esophageal (cardiac) sphincter controls the exit of food from the esophagus
to the stomach. It prevents the food in the stomach from moving back up the esophagus
by contracting. Heartburn occurs when the sphincter is not closed properly, because
the food backs up into the esophagus, and the acid coating it causes a burning
sensation. Heartburn often occurs during pregnancy because the digestive organs are
displaced far upward.
m o u t h a n d e s o p h a g u s q u i z
![]() Test your knowledge on the mouth. Click on next to start the quiz, or move
on to the next section to skip the quiz.
Test your knowledge on the mouth. Click on next to start the quiz, or move
on to the next section to skip the quiz.
A pain often described as heartburn actually has nothing to do with the heart!
back to top